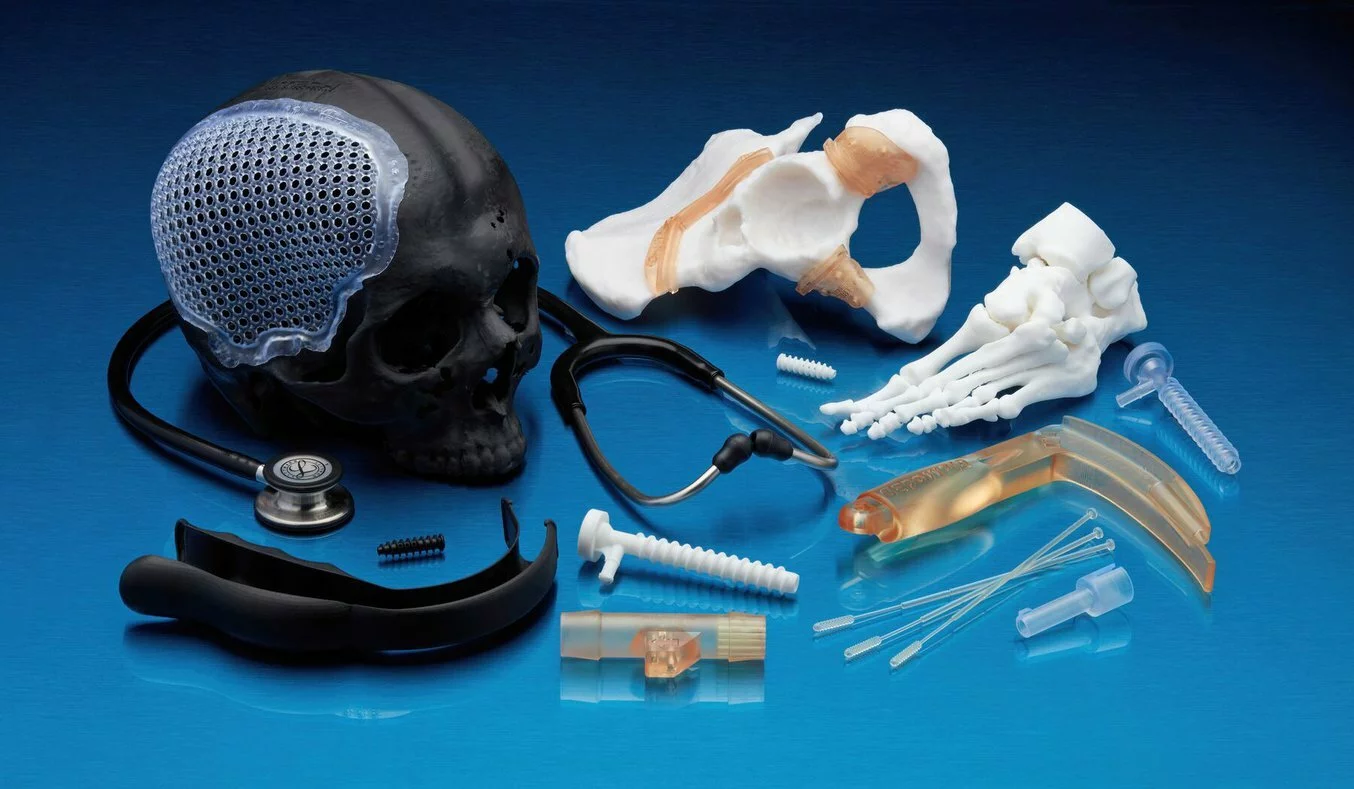
1. Patient-Specific Implants and Prosthetics:
One of the most notable applications of 3D printing in healthcare is the creation of patient-specific implants and prosthetics. Surgeons can now design and produce implants tailored to an individual’s unique anatomy, ensuring a precise fit and optimal functionality. This level of customization not only enhances patient outcomes but also accelerates recovery times.
2. Complex Surgical Planning and Training Models:
3D printing facilitates the development of intricate surgical models, enabling surgeons to meticulously plan and practice complex procedures before entering the operating room. This technology has proven invaluable in training medical professionals, reducing surgical risks, and improving overall procedural outcomes.
3. Bioprinting for Tissue Engineering:
The field of bioprinting has opened new frontiers in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Using a combination of cells, growth factors, and biomaterials, 3D bioprinting allows for the fabrication of living tissues and organs. This breakthrough holds immense potential for transplantations, reducing organ donor shortages and the risk of transplant rejection.
4. Customized Drug Delivery Systems:
3D printing has paved the way for the development of personalized drug delivery systems. By tailoring the structure and composition of pharmaceuticals to individual patient needs, healthcare professionals can optimize treatment regimens, enhance drug efficacy, and minimize side effects.
5. Anatomical Models for Education and Communication:
Medical professionals are leveraging 3D printing to create anatomically accurate models for educational purposes and patient communication. These models aid in explaining complex medical conditions to patients, enhancing their understanding and involvement in the decision-making process.
6. Dental Applications:
In dentistry, 3D printing has become instrumental in the fabrication of crowns, bridges, and even customized dental implants. The precision afforded by 3D printing technology ensures a perfect fit, improving patient comfort and overall oral health outcomes.
7. Point-of-Care Manufacturing:
3D printing enables point-of-care manufacturing of medical devices and components, reducing the dependency on traditional supply chains. This is particularly crucial in emergency situations or remote healthcare settings, where immediate access to specific tools or equipment can be life-saving.